191
Political Socialization in Youth: The Examination of The Relationship Between Civic Engagagement and Mass Media
JOURNAL OF YOUTH RESEARCHES
dents. Three education level groups (low, medium and high) were formed. More than half
of the research group (69%) was in high education group.
“Personel Data Sheet” was developed to measure socio-demographic variables (gender,
age, education level) and mass media use. It included a question regarding the type of
media used to follow news and the participants were allowed to choose more than one
type of media. The frequency of following news and social media use to express opinions
on political and current events was measured with subsequent questions.
Civic engagement was measured with “Civic Engagement Scale” consisting of 12 items.
The scale was formed by combining “Expectations for Civic Engagement Scale” (e.g.,
“Vote on a regular basis”) and “Political Voice Scale” (e.g., “Contact a newspaper, radio,
or TV talk show to express your opinion on an issue.”). The scales were developed by
Flanagan, Syvertsen and Stout (2007). Participants were asked to indicate how often (3 =
Very often, 2 = Sometimes, 1 = Never) they engaged in civic activities in the past. Cron-
bach’s alpha was .83.
The measures were administered to participants individually. The participants took part
in the study were volunteers and gave permission for the data to be used in the study.
The survey lasted approximately 40 minutes. In the study “relational screening model”
(Karasar, 2011) was used. The relationship between research variables were analyzed
with t-tests, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and hierarchical multiple regression.
The significance level was set at .05 for all analyses.
Results
The descriptive statistics for research variables are presented in Table 1. Most of the
participants (78.5%) indicated that they voted on regular basis. The half of the research
group was doing volunteer work (50.5%) and signing a petition (53.6%) occasionally.
More than the half of the participants mentioned that they had never contacted someone
in government (68.1%), a newspaper, radio, or TV talk show (63.8%) to express their
opinions on an issue.
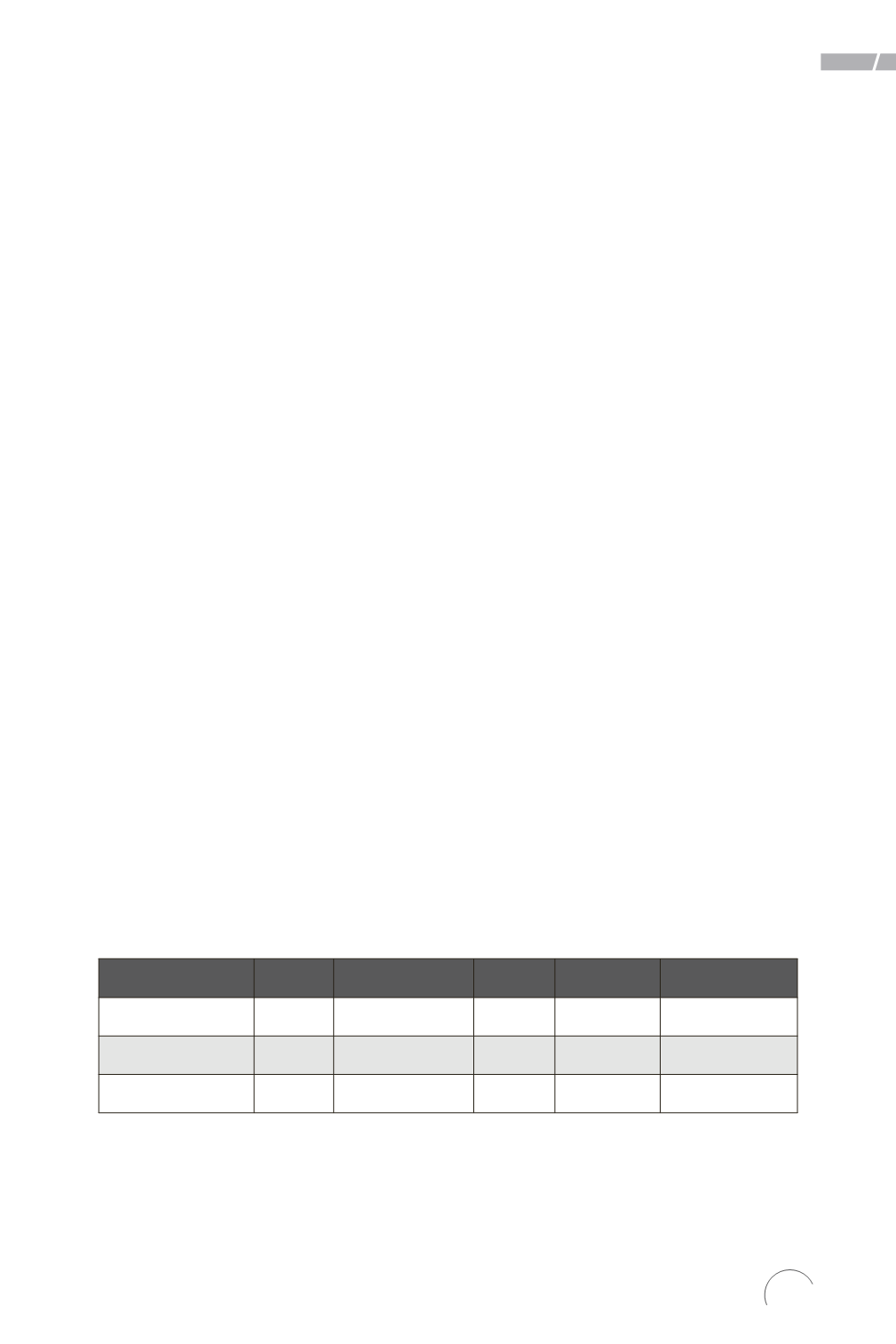
Table 1. Descriptive Statistics for Research Variables (N = 549)
Variables
X̅
Median
Mode
SD
S²
Civic Engagement
10.47
10.00
8.00
4.79
22.91
Following News
2.27
3.00
3.00
0.97
0.94
Social Media Use 2.33
3.00
0
1.91
3.64
53.6% of the participants were following news on daily basis. The frequency of media use
varied depending on the type of mass media. The Internet was used the most (75.8%),
followed by television (66.8%) and newspaper (43.9%). 57 participants were identified as
showing no interest in news. 64.3% of the participants were using social media as means


