193
Political Socialization in Youth: The Examination of The Relationship Between Civic Engagagement and Mass Media
JOURNAL OF YOUTH RESEARCHES
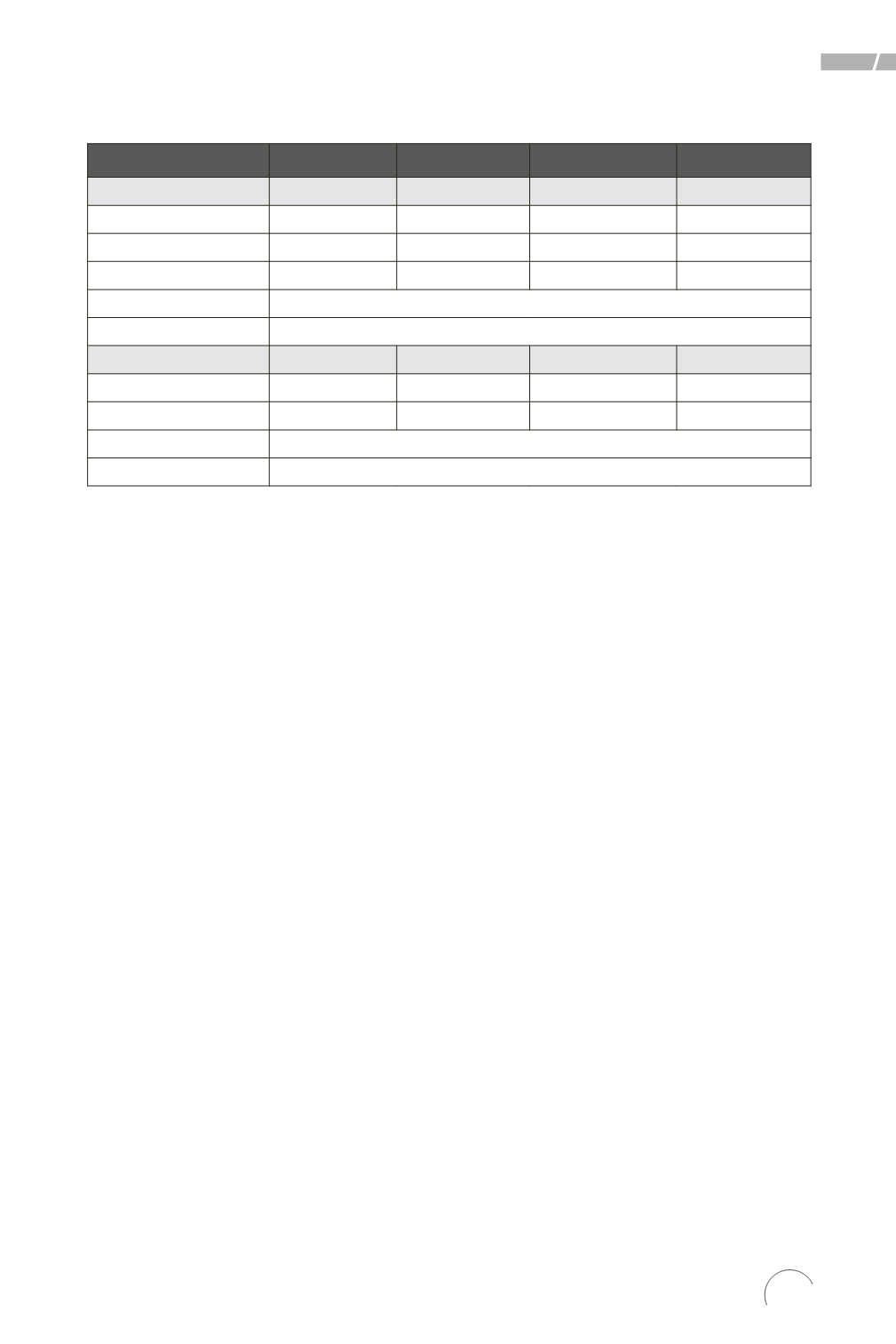
Table 2. Hierarchical Multiple Regression Analyses Predicting Civic Engagement
Variables
b
SH b
β
t
Step 1
Gender
0,65
0,42
,07
1,56
Age
-0,06
0,12
-,02
-0,52
Education
-1,09
0,29
-,16
-3,71**
∆R²
,03**
∆F
6,35
Step 2
Following News
0,52
0,22
,11
2,35*
Social Media Use
0,60
0,11
,24
5,31**
∆R²
,09**
∆F
26,16
N = 549; * p < ,05; ** p < ,001
Political, economic and social changes influence expectations from life, goals in life and the
responsibilities of young people. Therefore, it is important to determine the factors playing
role in political socialization of young people. In the present study, political socialization was
examined by assessing civic engagement. The aim of the study was to determine effects of
mass media use on civic engagement.
The frequency analysis of civic engagement by type of activity showed that young people con-
sidered voting as a responsibility of citizens. Most of the participants indicated that they were
voting on regular basis but they did not prefer expressing their opinions on social and political
matters via other channels as much. Young people were found to be moderately involved in
community issues such as health or safety and volunteer work. Men were found to be more
involved in civic activities than women. Although it has been argued that gender differences
have declined in recent years (Quintelier, 2011), it is shown that gender differences still exist in
terms of civic engagement. Gender socialization may account for these differences.
Consistent with previous studies (McLeod & Shah, 2009), the Internet was identified as the
type of mass media mostly used by young people to follow news. Most of the participants
were also using the Internet to express opinions on political and social matters. The wide-
spread use of the Internet to access information and for political communication among Turk-
ish young people suggests that the Internet is an important factor in their political socialization.
In spite of low rate of following news on printed version of newspaper, it was found to be
strongly related to civic engagement. Young people who read newspapers reported en-
gaging in more civic activities than those who did not. Following news via television or the
Iinternet did not lead to the same results. In some studies (e.g., Norris, 1996; Shah, McLeod
& Yoon, 2001), the positive relationship between newspaper and civic engagement has been
shown to be stronger than the relationship of television with civic engagement.
However, it has been indicated that the Internet is more effective than any other media in
terms of political interest and civic engagement of young people (Bachman, Kaufhold, Lewis


